良好的解决方案
Dr. Wiacek的实验室, the Medical Acoustics for Global health Imaging and Clinical translation (MAGIC) lab, continues strengthening SECS' expertise in biomedical imaging and AI.
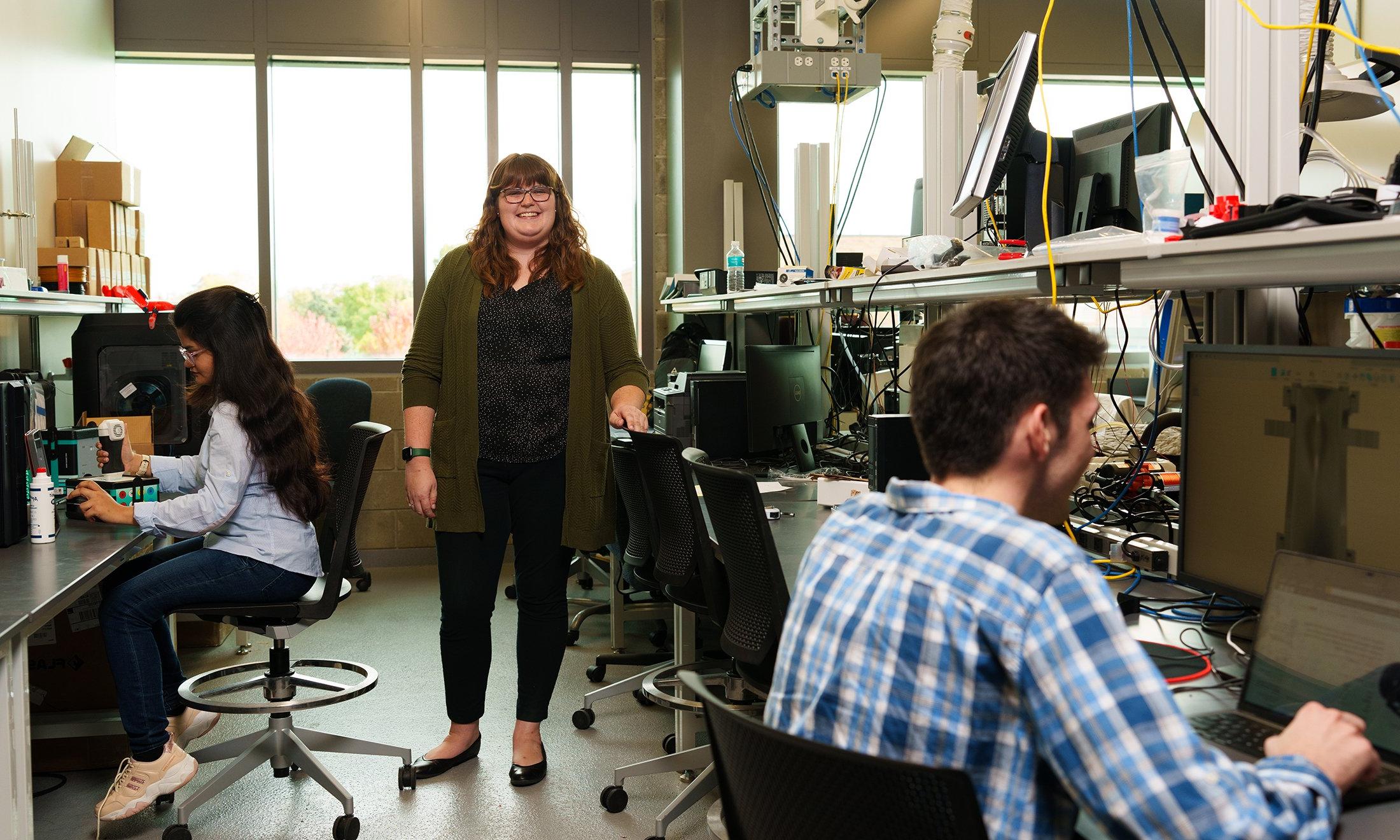

Rehnuma Hasnat (M.S.) and undergraduate bioengineering students Luc Taburet and Molly Vue (not pictured) work with Dr. Wiacek on the project that pairs artificial intelligence with ultrasound and elastography to improve the diagnosis and screening for breast cancer.
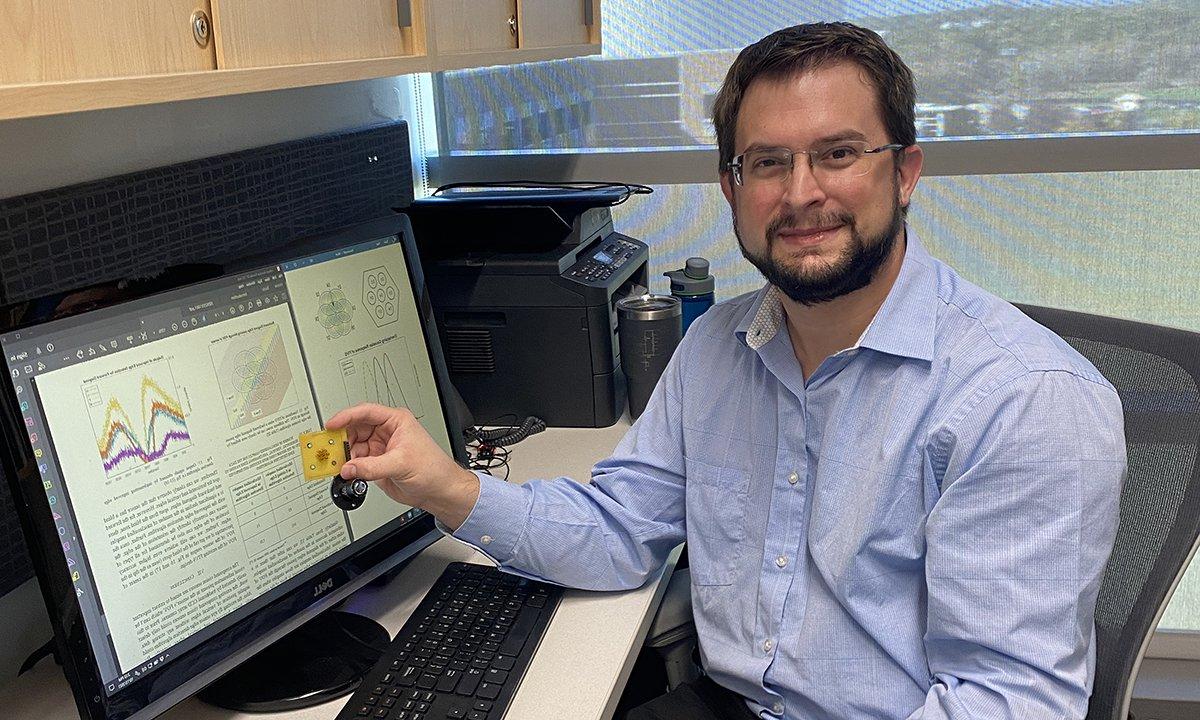
“通过我的研究, I strive to improve ultrasound technologies to create a new paradigm of acoustic-based screening methods for various diseases,Alycen Wiacek说, Ph.D., 俄亥俄州立大学助理教授, who works across two departments — the 生物工程系 and the Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering. “When combined with the correct hardware for signal detection and software for image combination and display, acoustic-based technologies can pave the way to a new generation of 无痛, 电离无辐射, 低成本的筛查方法,她补充道.
已经是博士了.D. 约翰霍普金斯大学的学生. Wiacek made considerable gains towards improving diagnostic quality and patient care by leveraging AI and other advanced signal processing techniques to develop systems in ultrasound and photoacoustic imaging. 她实现了一种新颖的深度学习架构, which learned physics-based features directly from raw ultrasound data, and created a novel photoacoustic imaging-based surgical guidance system for safer hysterectomy procedures.
在韦德体育app官网的第二年. Wiacek的实验室, the Medical Acoustics for Global health Imaging and Clinical translation (MAGIC) lab, continues strengthening SECS expertise in biomedical imaging and AI.
这是她目前的一个项目, supported by a grant from NASA through the Michigan Space Grant Consortium, focuses on the design of a digital optical and acoustic model of thrombosis. 更通俗的说法是血凝块, this model can be used to determine the optimal combination of quantitative image-based features to characterize blood clots over time.
“In 2019, a clot was found blocking the internal jugular vein of an astronaut while in space, prompting investigations into the impact of microgravity on thrombosis. 比如国际空间站, 做出如此关键的诊断所需的资源有限. 超声是这种检测的理想成像方法, but standard brightness mode (B-mode) ultrasound alone cannot quantitatively track blood clots over time or characterize them,” Dr. Wiacek解释说.
定量超声, 另一方面, can leverage the acoustic scattering properties of tissue to understand and characterize aspects of tissue microstructure. 结合光声成像, 哪一种利用了组织的光吸收特性, it has the potential to non-invasively provide quantitative information about the state and composition of the blood clot. 长期, these quantitative methods could be implemented in ex vivo and eventually in vivo settings, enabling monitoring of thrombosis over time in resource-limited settings in space and on Earth.
另一个研究领域. Wiacek is currently investigating pairs artificial intelligence with ultrasound and elastography to improve the diagnosis and screening for breast cancer.
弹性成像, which relies on the measurement of tissue motion before and after a small applied force, 是一种很有前途的方法来补充标准b超. It enables the assessment of the stiffness of masses embedded in tissue. 然而, both the B-mode and elastography images still suffer from noise and artifacts caused by wave propagation through tissue layers.
“By adding specific types of noise to simulated ultrasound and elastography images we can simulate real clinical imaging scenarios. We then train the network by giving it both the noisy image and the clean image, allowing it to learn what the noise looks like and how to remove it. 因此, 当给网络一个新的图像, it is able to effectively remove the noise and improve the overall image quality.博士说。. Wiacek.
“The neural network we are designing leverages information from both the traditional B-mode ultrasound image and the elastogram to improve image quality in both modalities and ultimately better visualize breast masses,Molly Vue说, 生物工程本科, 她和博士一起工作. Wiacek on the project and has recently won the Undergraduate Poster Presentation Award in Engineering at the 2023 Sigma Xi International Forum on 研究 Excellence.
The goals of the study are to create a dataset of simulated and phantom ultrasound and elastography images and develop an optimized network architecture to improve image quality. 在这项研究的结论中. Wiacek plans to release all code and datasets publicly, enabling future benchmark evaluations. 本研究由公开大学研究委员会资助.
“通过适当的工程设计, 基于声学的技术成本低, 无痛, 和便携, 使它们成为许多疾病筛查解决方案的未来. Dr. Wiacek的工作正在实现这一未来. Through creating acoustic-based screening hardware using multimodal integration techniques, 优化硬件以无缝过渡到诊所, 开发和优化算法,以获得更好的图像显示, 建立人工智能模型, 在一起, 她正在塑造公平解决方案的未来,Shailesh Lal说, Ph.D.生物工程系教授、系主任.
Dr. Wiacek’s research is closely tied to the missions of several groups within the National Science Foundation and the National Institute of Health. For more information about her research and current projects, please visit the lab website at www.秒.奥克兰.edu/ ~ awiacek

 2023年12月20日
2023年12月20日 Arina Bokas著
Arina Bokas著

